Contents
CSCS Working at Heights Test

Loading test...
- Answered
- Flagged
Operatives and Specialists - Working at Height ([year])
You need to answer at least 36 out of 40 questions correctly to pass the Working at Height Test for Operatives and Specialists. Answers may be reviewed after each question or at the end of the test. Good luck!
Attention!
Do you wish to proceed?
1687 votes - average 4.7 out of 5
Leave a comment
CSCS Working at Heights Test Questions and Answers (Printer-Friendly)
List of questions in above test (quick view). Click question box to reveal correct answer.
1. When it comes to construction site fatalities, what rough proportion are the result of falls from height?
Give ONE answer
A A negligible proportionB Half
C One quarter
D One tenth
Correct Answer: B Half
Explanation: About half of construction site fatalities are the result of falls from height.
Explanation: About half of construction site fatalities are the result of falls from height.
2. What is ONE common cause of falls from height?
Give ONE answer
A Using incorrect equipmentB Working in wet weather
C Working under the influence
D Working without safety equipment
Correct Answer: A Using incorrect equipment
Explanation: Using incorrect equipment is a common cause of falls from height.
Explanation: Using incorrect equipment is a common cause of falls from height.
3. Why are non-fatal falls from height so dangerous?
Give ONE answer
A They can cause a site to be closed downB They can cause life-changing injuries, and affect your ability to earn a living
C They can incur huge fines
D They can raise your insurance premium
Correct Answer: B They can cause life-changing injuries, and affect your ability to earn a living
Explanation: Falls from height can cause serious, debilitating injuries.
Explanation: Falls from height can cause serious, debilitating injuries.
4. Where MIGHT a risk assessment be conducted for the risk of falling from height?
Check ALL that apply
A Working aloneB Working in an excavation
C Working next to an excavation
D Working on a fragile roof
Correct Answer: B Working in an excavation, C Working next to an excavation, D Working on a fragile roof
Explanation: Any situation in which a harmful fall might take place may require a risk assessment. This includes work inside or next to excavations.
Explanation: Any situation in which a harmful fall might take place may require a risk assessment. This includes work inside or next to excavations.
5. Where MUST a risk assessment be conducted for the risk of falling from height?
Give ONE answer
A Any work at height where fall protection measures cannot be put in placeB Any work taking place above a height of 2 metres
C Anywhere where work at height is taking place
D Where work poses a risk to the public
Correct Answer: C Anywhere where work at height is taking place
Explanation: A risk assessment must be conducted for all work taking place at height.
Explanation: A risk assessment must be conducted for all work taking place at height.
6. How can a worker determine the best course of action to follow when working at height?
Give ONE answer
A Assess the situation and proceed in the safest possible wayB Find the fastest way to get the job done
C Refer to past experience with similar jobs
D Refer to the hierarchy of control
Correct Answer: D Refer to the hierarchy of control
Explanation: The hierarchy of control should be consulted when deciding what to do at height.
Explanation: The hierarchy of control should be consulted when deciding what to do at height.
7. What is ONE example of collective protection?
Give ONE answer
A A flat roofB Harness
C Parapet walls
D Scaffolding
Correct Answer: D Scaffolding
Explanation: Scaffolding is one example of collective protection.
Explanation: Scaffolding is one example of collective protection.
8. What is ONE example of personal protection?
Give ONE answer
A AirbagsB Harness and a lanyard for fall-arrest
C Safety netting
D Scaffolding
Correct Answer: B Harness and a lanyard for fall-arrest
Explanation: A harness with a fall-arrest lanyard is one example of personal protection
Explanation: A harness with a fall-arrest lanyard is one example of personal protection
9. What is the FIRST option you must consider according to the hierarchy of control?
Give ONE answer
A How to avoid work at heightB How to prevent a fall happening
C How to use collective protection to limit the consequences of falling
D How to use personal protection to limit the consequences of falling
Correct Answer: A How to avoid work at height
Explanation: Your first consideration must be how to avoid working at height.
Explanation: Your first consideration must be how to avoid working at height.
10. What should be the last resort according to the hierarchy of control?
Give ONE answer
A Not working at heightB Preventing a fall from happening in the first place
C Using collective protection to limit the consequences of falling
D Using personal protection to limit the consequences of falling
Correct Answer: D Using personal protection to limit the consequences of falling
Explanation: Personal protection used to limit the consequences of falling should be a last resort.
Explanation: Personal protection used to limit the consequences of falling should be a last resort.
11. Which ONE of the following offers adequate edge protection?
Give ONE answer
A NettingB Plastic barriers
C Rope
D Temporary guardrails
Correct Answer: D Temporary guardrails
Explanation: Edge protection must be rigid enough to stop people falling. Netting, plastic barriers, and rope are usually insufficient.
Explanation: Edge protection must be rigid enough to stop people falling. Netting, plastic barriers, and rope are usually insufficient.
12. When should you be asked to use a harness and fall-arrest lanyard?
Give ONE answer
A At all timesB If scaffolding cannot be installed
C If you are afraid of heights
D Only as a last resort
Correct Answer: D Only as a last resort
Explanation: Harnesses and fall-arrest lanyards should only ever be used as a last resort.
Explanation: Harnesses and fall-arrest lanyards should only ever be used as a last resort.
13. You are asked to quickly fix a beam where no fall protection measures have been put in place. What should you do?
Give ONE answer
A Ensure trained colleagues are around to spot youB Never work where there is no fall protection in place
C Only proceed if you are satisfied the risk of falling is low
D Use a ladder if possible
Correct Answer: B Never work where there is no fall protection in place
Explanation: Do not work on structures without fall protection.
Explanation: Do not work on structures without fall protection.
14. You are working on a flat roof. How should you protect yourself from falls?
Give ONE answer
A Always work in pairsB Attach your harness to a secure point on the roof
C Install a guard rail and toe board
D Install netting at the edge of the roof
Correct Answer: C Install a guard rail and toe board
Explanation: A guardrail and toe board is the best way to protect yourself from falls in this situation.
Explanation: A guardrail and toe board is the best way to protect yourself from falls in this situation.
15. Why do mobile access towers often cause accidents?
Give ONE answer
A The wheels often break under pressureB They are an inherently high risk structure
C They are often used or constructed incorrectly, which makes them unstable
D They are prohibited for use on construction sites, but often used anyway
Correct Answer: C They are often used or constructed incorrectly, which makes them unstable
Explanation: Mobile access towers are convenient and safe pieces of equipment. However, they are often built or used in such a way that they become unstable.
Explanation: Mobile access towers are convenient and safe pieces of equipment. However, they are often built or used in such a way that they become unstable.
16. With a mobile access tower, why is it dangerous to install the platform too high?
Give ONE answer
A Because equipment will be at greater risk of fallingB Because the guard rails will not provide adequate protection
C Because this increases the harm from falling
D Because this makes the structure less stable
Correct Answer: B Because the guard rails will not provide adequate protection
Explanation: Guard rails will not be high enough if the platform is put in too high.
Explanation: Guard rails will not be high enough if the platform is put in too high.
17. Which of the following rooves is LEAST likely to be fragile?
Give ONE answer
A A concrete roofB A tiled roof
C A wired glass roof
D An asbestos sheet roof
Correct Answer: A A concrete roof
Explanation: Many sorts of roofing can create fragile surfaces.
Explanation: Many sorts of roofing can create fragile surfaces.
18. When working on a mobile elevating work platform, what is ONE thing that must be ensured?
Give ONE answer
A That the area is quietB That the platform is clean
C That the wheels are locked
D That the wheels are properly oiled
Correct Answer: C That the wheels are locked
Explanation: The wheels must be locked before work can safely begin.
Explanation: The wheels must be locked before work can safely begin.
19. You need to remove a protective cover to begin work. What TWO measures must be in place?
Give TWO answers
A There must be nobody else around B You must be authorised to remove the cover
C You must be sure there is no risk of falling
D You must have an emergency radio
E You must have fall protection when the cover is removed
Correct Answer: B You must be authorised to remove the cover, E You must have fall protection when the cover is removed
Explanation: You must be authorised to remove any covers, and protected from falls whilst the cover is removed.
Explanation: You must be authorised to remove any covers, and protected from falls whilst the cover is removed.
20. Where must you NOT use a mobile elevating work platform?
Give ONE answer
A On asphalt surfacesB On busy roads
C On ground that is soft or uneven
D On private property
Correct Answer: C On ground that is soft or uneven
Explanation: Ground must be stable and firm.
Explanation: Ground must be stable and firm.
21. What PPE item must workers on a mobile elevating work platform wear at all times?
Give ONE answer
A A harness and lanyardB A respiratory mask
C Footwear with good grip
D Warm clothing
Correct Answer: A A harness and lanyard
Explanation: A harness is the most important item a worker on this piece of equipment must wear.
Explanation: A harness is the most important item a worker on this piece of equipment must wear.
22. When wearing a harness on a mobile elevating work platform, where should the lanyard be attached?
Give ONE answer
A To a secure point on the buildingB To a specified anchor point
C To the bolt point on the underside of the platform
D To the nearest handrail
Correct Answer: B To a specified anchor point
Explanation: Always use the specified anchor point.
Explanation: Always use the specified anchor point.
23. What are TWO key reasons why people do not notice when a roof is fragile?
Give TWO answers
A People are not paying attention B The signage is out of date
C There is no signage in place
D Weathering, dirt, or paintwork conceal its condition
Correct Answer: C There is no signage in place, D Weathering, dirt, or paintwork conceal its condition
Explanation: A lack of appropriate signage, and the presence of factors that affect its appearance, may stop people noticing that a roof is fragile.
Explanation: A lack of appropriate signage, and the presence of factors that affect its appearance, may stop people noticing that a roof is fragile.
24. What is ONE good way to mitigate the risks of working on a fragile roof?
Give ONE answer
A Add appropriate signageB Clean the roof
C Ensure your weight is balanced on the underlying beams
D Use a mobile elevating work platform to work on the roof from below
Correct Answer: D Use a mobile elevating work platform to work on the roof from below
Explanation: Where possible, you should avoid working on top of fragile rooves.
Explanation: Where possible, you should avoid working on top of fragile rooves.
25. What is best practice when beginning work on a roof?
Give ONE answer
A Assume it contains asbestosB Assume it is fragile, unless a competent person assesses it to be safe
C Assume it is safe, unless a competent person assesses it to be fragile
D Assume you must wear a harness at all times
Correct Answer: B Assume it is fragile, unless a competent person assesses it to be safe
Explanation: Always assume rooves are fragile, unless a competent person assesses it to be otherwise
Explanation: Always assume rooves are fragile, unless a competent person assesses it to be otherwise
26. Which of the following ladders ARE suitable for use on construction sites?
Give TWO answers
A Any ladder may be suitableB Class 1 Industrial
C EN 131 Domestic
D EN 131 Trade and Industrial
Correct Answer: B Class 1 Industrial, D EN 131 Trade and Industrial
Explanation: Never use domestic grade ladders on a construction site.
Explanation: Never use domestic grade ladders on a construction site.
27. Under what ONE of the following conditions might a ladder be appropriate?
Give ONE answer
A For light tasks that last no longer than 30 minutesB When materials or equipment only need to be carried a short way
C When you need a low-level work platform
D When you will be using pressure
Correct Answer: A For light tasks that last no longer than 30 minutes
Explanation: Ladders should be used rarely, for light and short-duration tasks, as a last resort.
Explanation: Ladders should be used rarely, for light and short-duration tasks, as a last resort.
28. How should you properly secure a ladder?
Give ONE answer
A Always have someone holding it at the bottomB Tie it at the bottom
C Tie it at the top
D Weight it with rocks
Correct Answer: C Tie it at the top
Explanation: Tying a ladder at the top is the best way to secure it.
Explanation: Tying a ladder at the top is the best way to secure it.
29. If a ladder has a wobbly rung, what should you do?
Give ONE answer
A Do not step on the faulty rungB Do not use it and report the fault to your supervisor
C Report it in the accident book
D Secure the rung and continue work if it is safe to do so
Correct Answer: B Do not use it and report the fault to your supervisor
Explanation: Equipment defects must always be reported.
Explanation: Equipment defects must always be reported.
30. When is it permissible to paint a ladder?
Give ONE answer
A If it has suffered cosmetic damageB If it needs to be more visible
C If it needs waterproofing
D Never
Correct Answer: D Never
Explanation: Painting ladders can obscure defects.
Explanation: Painting ladders can obscure defects.
31. Is this ladder positioned at a safe angle?
Give ONE answer
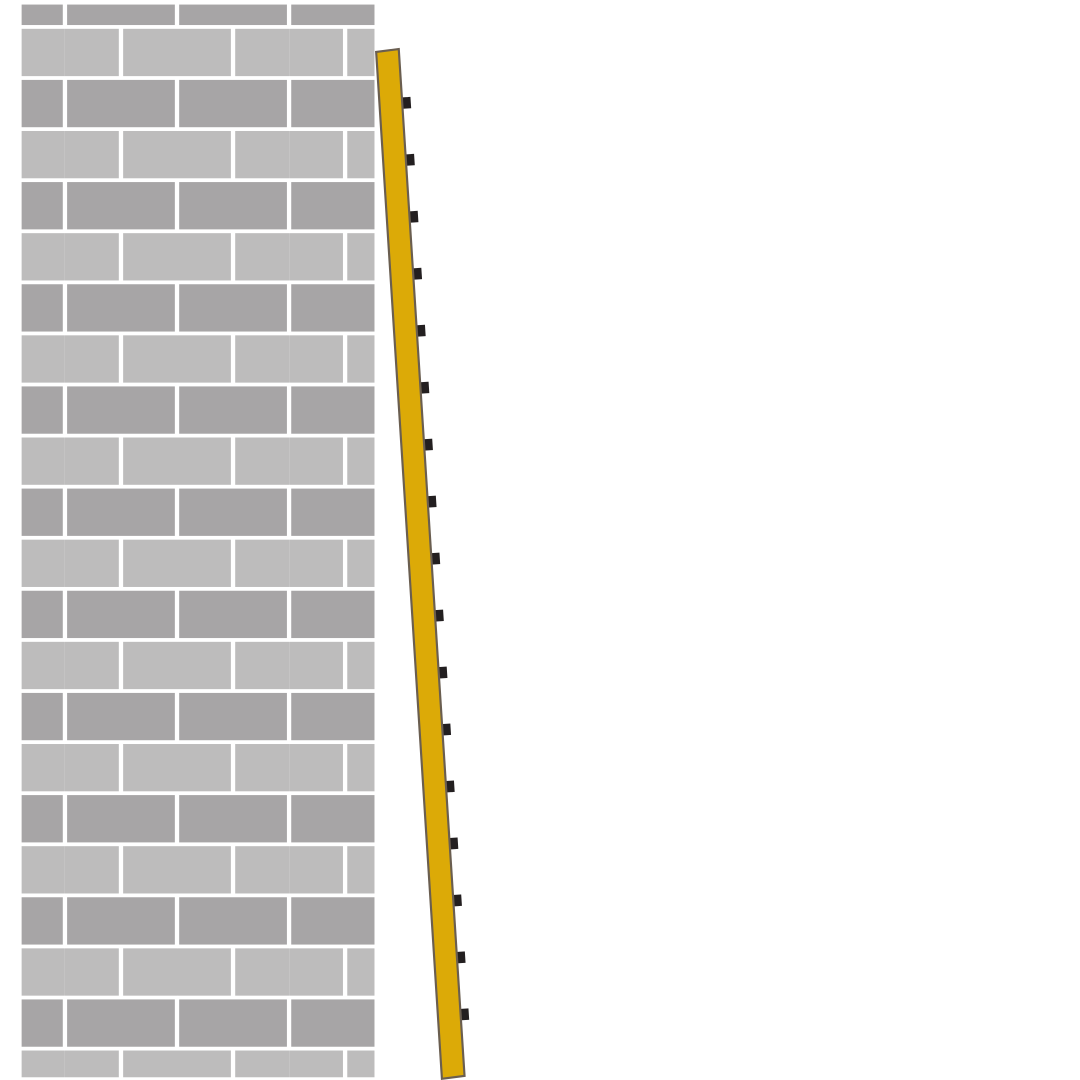
B Yes
Correct Answer: A No
Explanation: This ladder is not safely positioned - it is too steep.
Explanation: This ladder is not safely positioned - it is too steep.
32. How should a stepladder be oriented?
Give ONE answer
A At 90 degrees from the work, so you have space to operateB At whichever angle gives you the best access for work
C So both the ladder and you are facing your work
D So both you and the ladder are facing away from your work
Correct Answer: C So both the ladder and you are facing your work
Explanation: Both you and the ladder must be facing the work.
Explanation: Both you and the ladder must be facing the work.
33. What is the safest ratio when positioning a ladder for work?
Give ONE answer
A One out, five upB One out, four up
C One out, three up
D Two out, four up
Correct Answer: B One out, four up
Explanation: A 1:4 ratio (one out, four up) creating an angle of 75 degrees is the safest position.
Explanation: A 1:4 ratio (one out, four up) creating an angle of 75 degrees is the safest position.
34. Which best describes a safe way of climbing a stepladder?
Give ONE answer
A Always attach your harness lanyard to the anchor pointB Always install fall protection
C Ensure at least three points of contact where possible
D Ensure at least two points of contact where possible
Correct Answer: C Ensure at least three points of contact where possible
Explanation: Where possible, always maintain three points of contact.
Explanation: Where possible, always maintain three points of contact.
35. What part of a stepladder must you not stand on?
Give ONE answer
A The bottom rungB The bottom three rungs, unless it is specially designed
C The top rung
D The top three rungs, unless it is specially designed
Correct Answer: D The top three rungs, unless it is specially designed
Explanation: Unless the stepladder has been specially designed, you must avoid using the uppermost rungs.
Explanation: Unless the stepladder has been specially designed, you must avoid using the uppermost rungs.
36. How can you find out a scaffold platform's safe load rating?
Give ONE answer
A You can check the signage or handover certificateB You can check with the contractor
C You can inspect the scaffolding for damage
D You can refer to the safe system of work
Correct Answer: A You can check the signage or handover certificate
Explanation: You can find this information on the signage and the handover certificate.
Explanation: You can find this information on the signage and the handover certificate.
37. You need to begin a task but the access ladder is barred off with tape. What should you do?
Give ONE answer
A Do not begin work, and consult your supervisorB Inspect the scaffolding for hazards, and continue if it appears safe
C Remove the tape so you can get through, but replace it behind you
D Remove the tape so you can safely access the scaffolding
Correct Answer: A Do not begin work, and consult your supervisor
Explanation: Never access scaffolding where signage indicates it is unsafe to do so.
Explanation: Never access scaffolding where signage indicates it is unsafe to do so.
38. A simple piece of scaffolding is interfering with your task's safety measures. What should you do?
Give ONE answer
A Adapt your safe system of work around the obstacleB Consult your supervisor
C Remove the piece and replace it at the end of your shift
D Remove the piece only for as long as required to complete your work
Correct Answer: B Consult your supervisor
Explanation: Scaffolding can only be adjusted or dismantled by competent and trained scaffolders.
Explanation: Scaffolding can only be adjusted or dismantled by competent and trained scaffolders.
39. What is the purpose of ground level controls in a mobile elevating work platform?
Give ONE answer
A They allow workers in the platform to concentrate on their taskB They allow workers with a better view to control the platform from below
C They are an emergency backup
D They make work more efficient
Correct Answer: C They are an emergency backup
Explanation: Ground level controls are for use in emergencies only.
Explanation: Ground level controls are for use in emergencies only.
40. Who is responsible for training and informing workers at height so they can operate safely?
Give ONE answer
A The HSEB The employees must take responsibility for this themselves
C The employer
D The on-site administration
Correct Answer: C The employer
Explanation: Employers must ensure all workers receive adequate instruction and information.
Explanation: Employers must ensure all workers receive adequate instruction and information.





