Fire kills and injures many people every year in the UK. On construction, demolition or refurbishment sites there can be a high risk of fire. Smoke and fire can spread rapidly and this risk can increase depending on the stage of the project. It is therefore important that you’re familiar with the various types of fire extinguishers – not only will it appear in your CSCS Test but you may also need to use one in the event of a fire. Click the Begin Test button to start the CSCS Mock Test Fire Extinguishers below.

- Answered
- Flagged
You need to answer at least 34 out of 38 questions correctly to pass the Fire Prevention and Control Test for Operatives and Specialists. Answers may be reviewed after each question or at the end of the test. Good luck!
Do you wish to proceed?
1914 votes - average 4.8 out of 5
Leave a comment
Fire Extinguishers Mock Test Questions (Printer-Friendly)
B The HSE
C The employees
D Your employer
Explanation: Your employer is responsible for providing and maintaining fire safety equipment.
B In a secure storage space, provided by your employer
C It does not matter, so long as they are handled correctly
D Near where they will be used
Explanation: Your employer must provide a safe storage space for flammable materials.
B Ensuring all workers in the area are aware of the activity
C Having a good water supply nearby
D Informing the HSE in advance
Explanation: Your employer should have in place a control system for hot work and this may include a hot-works permit.
B In areas where flammable materials are not in use
C In permitted areas designated by your employer
D Nowhere
Explanation: Smoking is only permitted in designated areas provided by your employer.
B Ensuring all your team are aware of any permits being acquired
C Knowing how and when to acquire them
D Taking the relevant tests to ensure you are aware of risks
Explanation: Employees should understand how and when to acquire hot work permits.
B Fuel
C Heat/ignition
D Oxygen
E Tinder
F Wood
Explanation: A fire can break out if fuel, oxygen, and heat or ignition are present.
B Heat and fuel
C Heat, oxygen, and fuel
D Oxygen and fuel
Explanation: Removing any one of these elements will put out a fire.
B Removing fuel
C Removing heat
D Removing oxygen
Explanation: A foam extinguisher smothers the fire by removing oxygen.
B They do not light well in smoky rooms, creating an evacuation risk
C They may overheat, creating an ignition risk
D They will explode in case of fire, creating an injury risk
Explanation: Lights, especially halogen lights, may become ignition risks if they overheat.
B Paint may have gotten on your tool, and if so this creates an ignition hazard
C The paint fumes may have created a dangerous atmosphere during that time. If your drill overheats, it may ignite the fumes.
D The paint fumes may have created a dangerous atmosphere during that time. You should be wearing appropriate RPE
Explanation: Paint pots and solvents left open create a potentially flammable atmosphere. An overheating power tool would be enough to set this on fire.
B Yes, if it is used only for burning welfare waste
C Yes, only if it has been cleared with the site management
D Yes, only if the site has a permit to do so
Explanation: Bonfires are only allowed if the site has a permit.
B There will be marshals instructing you during evacuation
C You are responsible for seeking this information out in advance
D You will be informed during site induction
Explanation: Fire evacuation procedure should be covered during site induction.
B Follow fire evacuation procedure
C Nothing - this is the mandated time for fire-alarm testing on construction sites
D Stop work and check with a supervisor whether this is a drill
Explanation: Treat all unexpected alarms as indicating a fire on-site. Immediately stop work and follow your site's evacuation procedure.
B There will be a bin for cigarette butts
C There will not be any cordons indicating the area is a combustion risk
D You will be informed during induction
Explanation: You will be informed of any smoking areas during your site induction.
B TRUE - the escape route must remain fixed over the project as per the original risk assessment
Explanation: Escape routes may change as the project develops. It is your responsibility to ensure you are aware of any changes.
B Because the work involved creates additional legal liability for your employer
C Because the work involved creates specific fire risks
D Because the work involved exposes you to harmful temperature levels
Explanation: Hot work permits help control and mitigate the additional fire risks created by these activities.
B It will be detailed in your induction handbook
C It will be detailed on the packaging of the relevant fire extinguisher
D The extinguisher will be located in your work area
Explanation: A hot works permit will tell you which fire extinguisher must be available.
B Continue to your next task
C Maintain fire watch if you are instructed to do so in your permit
D Maintain fire watch until all materials and tools have cooled
Explanation: Your hot works permit will detail how long fire watch must be maintained after the activity is complete.
B However soon is specified in the hot works permit
C Where the hot works permit has been correctly followed, no further checks are needed
D Within 1 hour
Explanation: You should always return at a later time to check the area. Precisely how long will be detailed in the hot works permit.
B Reach a safe point to stop work and make your way to the fire assembly point
C Wait for confirmation that evacuation is necessary
D Wait for confirmation that the alarm is not a test or a drill
Explanation: When the alarm sounds you should stop work immediately and head to the fire assembly point.
B It will be clearly displayed
C You will be informed only if you have been trained to use it
D You will be told during induction
Explanation: Your site induction will include information on where equipment is located.
B It can be ignited at temperatures lower than 55 degrees Celsius
C It can be ignited without being exposed to sparks or naked flames
D It cannot be extinguished with water once ignited
Explanation: A highly flammable liquid is one that can ignite at temperatures lower than 32 degrees Celsius.
B In a closed container
C In a plastic container
D In an impact-proof container
Explanation: Closed containers must be used to store flammable liquids.
B Clear it up immediately
C Clear the area until your supervisor can assess the risk
D Record it in the incident book
Explanation: You must immediately clear up any spillages of flammable liquids.
B Silty water
C Solvents
D Thinners
Explanation: Besides silty water, these are all examples of flammable liquids.
B In an insulating casing
C Sideways
D Upright
Explanation: Compressed gas must be stored upright.
B To limit the damage caused by shrapnel in case of explosion
C To make it harder to steal
D To prevent the buildup of vapours in case of leakage
Explanation: Storing LPG in cages means there will not be a build-up of vapours in case of leaks.
B Whether the basement is the correct temperature, and has proper ventilation
C Whether the site is licensed to store flammable liquids
D Whether there is a safer alternative, as underground storage should be a last resort
Explanation: LPG cannisters should NEVER be stored below ground, for example in basements or cellars.
B The valve is rusting
C They are being stored at too low a temperature
D They are leaking
Explanation: Frost around the valve indicates that an LPG cylinder is leaking.
B They have different coloured cannisters
C They have different coloured hoses
D They have different coloured panels
Explanation: Extinguishers of each type are given a different coloured panel.
B Blue (powder)
C Cream (foam)
D Red (water)
E Yellow (wet chemical)
Explanation: Electrical fires can be put out with blue (powder) and black (carbon dioxide) extinguishers. You must NOT use any other extinguisher.
B To fight small fires
C To help a person escape
D To limit the spread of large fires
E To meet legal regulations
Explanation: Extinguishers are for the purpose of helping a person escape and fighting very minor fires.
B Bigger than a wastepaper bin
C Happening by a window
D Taller than you
Explanation: Extinguishers are to be used on small fires only - as a rule of thumb, fires no bigger than a wastepaper bin.
B Keep detailed personal notes of your activities
C Keep in regular remote contact with your supervisor, e.g. through radio
D Wear a bodycam
Explanation: You may be asked to keep in regular contact.
B That you are wearing a high-visibility vest
C That you do not make excessive noise
D That you do not use tools for longer than ten minutes at any time
Explanation: You should always ensure the escape route is kept clear of unnecessary clutter.
B Insufficiently monitored hot works
C Unclear fire safety inductions
D Untidy work areas
Explanation: Hot works and cluttered workspaces are common fire hazards.
B Enough to last a week, to reduce hazards created when transporting the liquid
C Only enough to complete the task at hand
D Only enough to last the day's shift
Explanation: You should never remove more liquid than is immediately required.
B Even at some distance from the cannister, the leak can be ignited and travel back
C The leak will create a flammable atmosphere in the area approximately 1m around it
D This is common, and not a cause for concern if correct precautions are taken
Explanation: LPG leaks can be ignited some distance from the cannister.
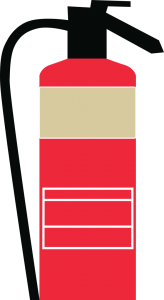
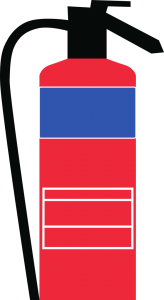
Fire Extinguishers Types and Colours
When using portable fire extinguishers it is vital that everyone is vigilant and any hot work is controlled. The table below shows the types of portable fire extinguishers and what to use them on.
| Extinguishing medium | Colour of panel | Where not to use |
| Water: for wood, paper, textile and solid material fires | Do not use on liquid, electrical or metal fires | |
| Foam: for liquid fires | Do not use on electrical or metal
fires |
|
| Powder: for liquid and electrical fires
Specialist dry powders: for metal fires |
Do not use on metal fires unless
M28 or L2 text is printed on extinguisher, which means it is suitable for metal fires |
|
| Carbon dioxide: for wood, paper, textiles, gaseous, liquid and electrical fires | Do not use on metal fires | |
| Wet chemical: for wood, paper, textile, cooking oil and solid material fires | Do not use on liquid, gas or electrical fires |
Note: dry powder extinguishers may be provided as well as or substituted for water, foam or carbon dioxide extinguishers. Extinguishers used to control Class 8 fires (flammable liquids) will not work on Class b fires (cooking oils) because of the high temperatures produced.
Fire extinguishers should only be used on very small fires (as a guide, no bigger than a waste paper bin) or to aid escape.