CITB Mock Test for Operatives

- Answered
- Flagged
You have 45 minutes to answer 50 multiple choice CSCS Health, Safety and Evironment Test questions for Operatives and Specialists. You need to answer at least 45 out of 50 questions correctly to pass. Answers may be reviewed after each question or at the end of the test. Good luck!
Do you wish to proceed?
2342 votes - average 4.6 out of 5
CSCS Test for Operatives and Specialists
Below are several free CSCS mock tests for operatives and specialists.
There are more than 1000 practice questions for Operatives and Specialists in these mock tests. All tests last for 45 minutes and have 50 questions which have been randomly selected from 16 categories.
Operatives Tests by Category
Specialist Activities
Below are several free mock tests for specialists.
If you are preparing for a specialist test, you also need to study the appropriate specialist activity, from those listed below. There are more than 500 specialists questions.
CITB Mock Test for Operatives Practice Questions (Printer-Friendly)
B Nothing - if the leader did not make it clear, it probably was not important
C Wait until the session is completed, then ask the induction leader
D Wait until the session is completed, then consult the handbook
Explanation: Always ask for information to be clarified during the session itself. If you found something unclear, it is possible that others did too.
B The board of directors
C The recruitment team
D The site manager
Explanation: The HSE must be informed of this injury.
B The date and time of the accident
C Your address
D Your name
Explanation: You are not required to provide details of your medical history. The book's purpose is to avoid future accidents.
B It has a yellow pallour
C It has no smell, taste, or colour
D It tastes sharp
Explanation: Carbon dioxide also has no taste, colour, or smell.
B To ensure workers are not discriminated against
C To ensure workers can see properly when using respiratory protective equipment
D To ensure workers have a clean criminal record
Explanation: Face fit tests check that respiratory protective equipment will work effectively.
B Filters for dust/particles
C Filters for gas/vapours
D Filters for moisture
E Filters for odour
Explanation: Masks typically use filters for gas/vapours, and dust/particles.
B It is not an effective strategy
C It prevents much of the dust from escaping into the air
D It reduces the risk of combustion
Explanation: Wet cutting is a common and effective strategy, as it stops much of the work-related dust escaping in the first place.
B It should be sprayed on the material periodically throughout the cutting
C It should be used afterwards, to clear dust from the material
D It should be used to douse the material before cutting, and sluice it afterwards
Explanation: You must apply water constantly to capture new dust as it is created.
B It is an oversight. Do not begin work until you have been given suitable RPE
C RPE is not required for this task, and you can begin working
D RPE is optional for this task, and you can begin working if you wish
Explanation: Never work without RPE if the job you are doing requires it.
B Get someone to supervise you when you first use it
C Use it as frequently as possible
D Use it without supervision to test how much you have absorbed
Explanation: When using a tool you have been recently trained on, always begin under supervision.
B You must inform your colleagues
C You must never use a power tool independently
D Your employer must ensure you are competent
Explanation: Your employer must ensure that you are competent to operate powered tools independently before you begin.
B Only use gentle pressure when cutting the tile
C Only use the tool for short periods of time
D Wait until the correct disc can be found
Explanation: Never use a disc or blade for a job it is not designed to do.
B Using a rotary diamond cutter
Explanation: A rotary diamond cutter is the safer option to protect your hearing.
B Compress them between two fingers, and insert them as deep as you can
C Push them in without rolling them, as this will damage the fibres and reduce their effectiveness
D Tightly roll them, and insert them deep into the ear canal
Explanation: Roll the plugs and insert them deep into the canal; this is easier if you pull the top of your ear to widen the canal.
B Continue working but monitor yourself for further symptoms
C Report your symptoms so better preventative measure can be put in place
D Stop all work and consult a doctor immediately
Explanation: Tingling fingers can be an early sign of HAVS, and suggest insufficient safety measures are in place. You must report this symptom before the condition worsens.
B You must catch any spillages by laying an absorbent mat or drip tray underneath
C You must cordon off the area
D You must keep a record of the incident
E You must use a leak-proof siphon
Explanation: Mitigate the risks of pollution by remaining distant from water sources and drains, and laying ground protection underneath.
B To allow solids to separate from the liquid
C To keep the substance well ventilated
D To reduce the risk of leakage
Explanation: This is to allow the sediment and liquid to separate, and be disposed of separately.
B That noise from the vehicles may drown out communication within the excavation
C That the weight of these vehicles may cause the excavation to collapse
D That workers exiting the excavation may be struck by on-site traffic
Explanation: Heavy vehicles operating too close to an excavation may weaken the walls, increasing the risk of collapse.
B The health and safety manager
C The site manager
D The workers who will be entering the excavation
Explanation: Excavations must be inspected by a competent person.
B Electricity
C Gas
D Water
Explanation: Electricity services are likely to be coloured red or black - but this is not always the case.
B Ensure the torch is not near any flammable items
C Ensure the torch is properly switched off
D Remove and isolate the torch
Explanation: Leaks from items like hoses and torches may go unnoticed. When not in use, they must be removed from confined spaces and isolated.
B The attendant, who must remain at the entrance to the space
C The health and safety manager
D The on-site manager
Explanation: An attendant must always man the entrance to a confined space, and is primarily responsible for setting the exit plan in motion.
B Harness
C Parapet walls
D Scaffolding
Explanation: Scaffolding is one example of collective protection.
B How to prevent a fall happening
C How to use collective protection to limit the consequences of falling
D How to use personal protection to limit the consequences of falling
Explanation: Your first consideration must be how to avoid working at height.
B The signage is out of date
C There is no signage in place
D Weathering, dirt, or paintwork conceal its condition
Explanation: A lack of appropriate signage, and the presence of factors that affect its appearance, may stop people noticing that a roof is fragile.
B Class 1 Industrial
C EN 131 Domestic
D EN 131 Trade and Industrial
Explanation: Never use domestic grade ladders on a construction site.
B The bottom three rungs, unless it is specially designed
C The top rung
D The top three rungs, unless it is specially designed
Explanation: Unless the stepladder has been specially designed, you must avoid using the uppermost rungs.
B They allow workers with a better view to control the platform from below
C They are an emergency backup
D They make work more efficient
Explanation: Ground level controls are for use in emergencies only.
B If no better PPE is available
C If sweeping up light wood dust
D Under no circumstances should they be used as PPE
Explanation: These masks do not meet the required RPE standards. They should not be used as RPE.
B Heat and fuel
C Heat, oxygen, and fuel
D Oxygen and fuel
Explanation: Removing any one of these elements will put out a fire.
B Do not enter the site until the HSE has inspected it
C Keep detailed notes in case you should need to make an insurance claim in future
D Proceed as normal, if the survey has been properly conducted
Explanation: Always assume asbestos may still be present - no survey can provide absolute certainty.
B Any party who has completed an advanced asbestos handling course
C Only a licensed contractor
D Only the HSE
Explanation: High risk materials can only be removed by a licensed contractor.
B When heated above body temperature
C When in sustained contact with bare skin
D When ingested
Explanation: Ingesting lead is highly dangerous.
B Make sure everything has been neatly put back in place
C Restock the items you have used from the kit
D Use spray disinfectant to clean anything inside that you have touched
Explanation: The person managing the first aid equipment must always be informed if it has been used.
B Nothing - the person in charge of managing it will be aware
C Report it in the accident book
D Restock the kit at the next opportunity
Explanation: If you notice the first-aid kit is not properly restocked, you must inform the person in charge of managing it.
B Yes - you are legally permitted to access safety records relevant to your on-site tasks
Explanation: The accident book must be kept confidential.
B Your face will begin to feel puffy, and you may suffer bouts of dizziness
C Your hands may begin to show redness, cracking, and itching
D Your hands will begin to swell
Explanation: Occupational dermatitis may begin to exhibit through redness, cracking, and itching in the hands.
B It may become gangrenous
C It may develop into septic ulcers
D It may spread to internal organs
Explanation: Contact dermatitis can develop into painful ulcers.
B A bacterial disease that affects the nervous system
C A bacterial infection that affects the skin
D A viral infection that affects the nervous system
Explanation: Tetanus affects the nervous system. It is a bacterial disease.
B You are fitting attic insulation
C You are fixing air conditioning
D You are laying concrete
Explanation: Legionella is contracted when a person breathes in vapour or mist from contaminated water.
B They should begin health surveillance
C They should help you access the support you need
D They should inform your team of your condition
Explanation: Your employer should confidentially offer you the support you need.
B Staff morale drops
C The number of resignations may increase
D The risk of accidents increases
Explanation: Fatigued workers are more likely to have accidents.
B Cancer
C Hernia
D Rupture
Explanation: Various injuries can result from manual handling, but diseases are uncommon.
B Sleep on your side
C Wear a neck brace
D Work on cultivating good posture
Explanation: Good posture at all times will help protect you against injury.
B If the load is expensive
C If the load is greasy
D If the load is hazardous
E If the load is urgently needed
Explanation: A safe system of work is designed to protect the safety of workers, not the cost or efficiency of a project.
B When there are not enough workers on hand to handle the load manually
C When there is reduced visibility
D Whenever possible, to reduce the risk of injury
Explanation: Lifting aids should be used whenever possible.
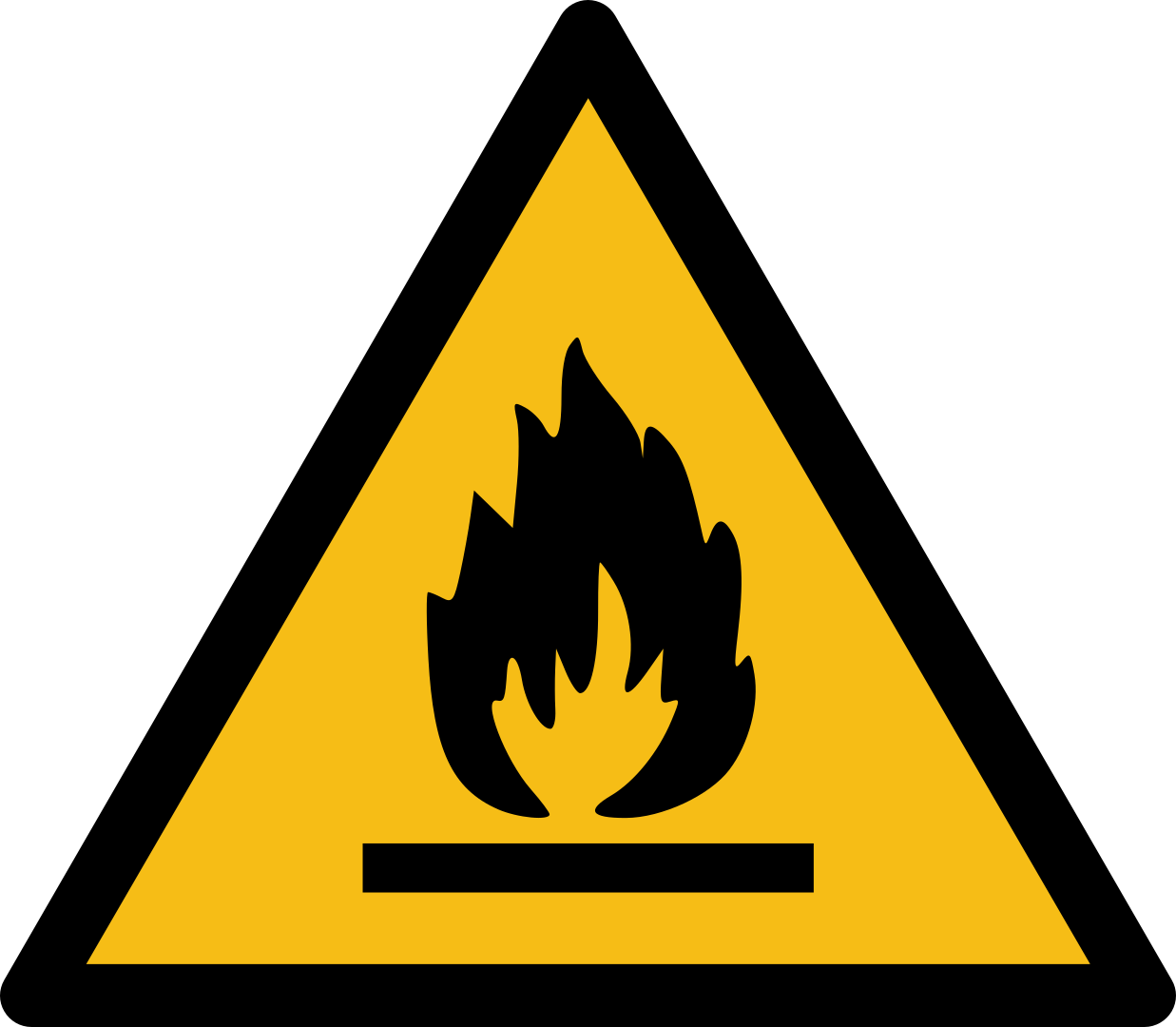

B Warning sign for fires in the vicinity
C Warning sign for flammable material
D Warning sign for waste being burned
Explanation: This is a warning sign for flammable materials.
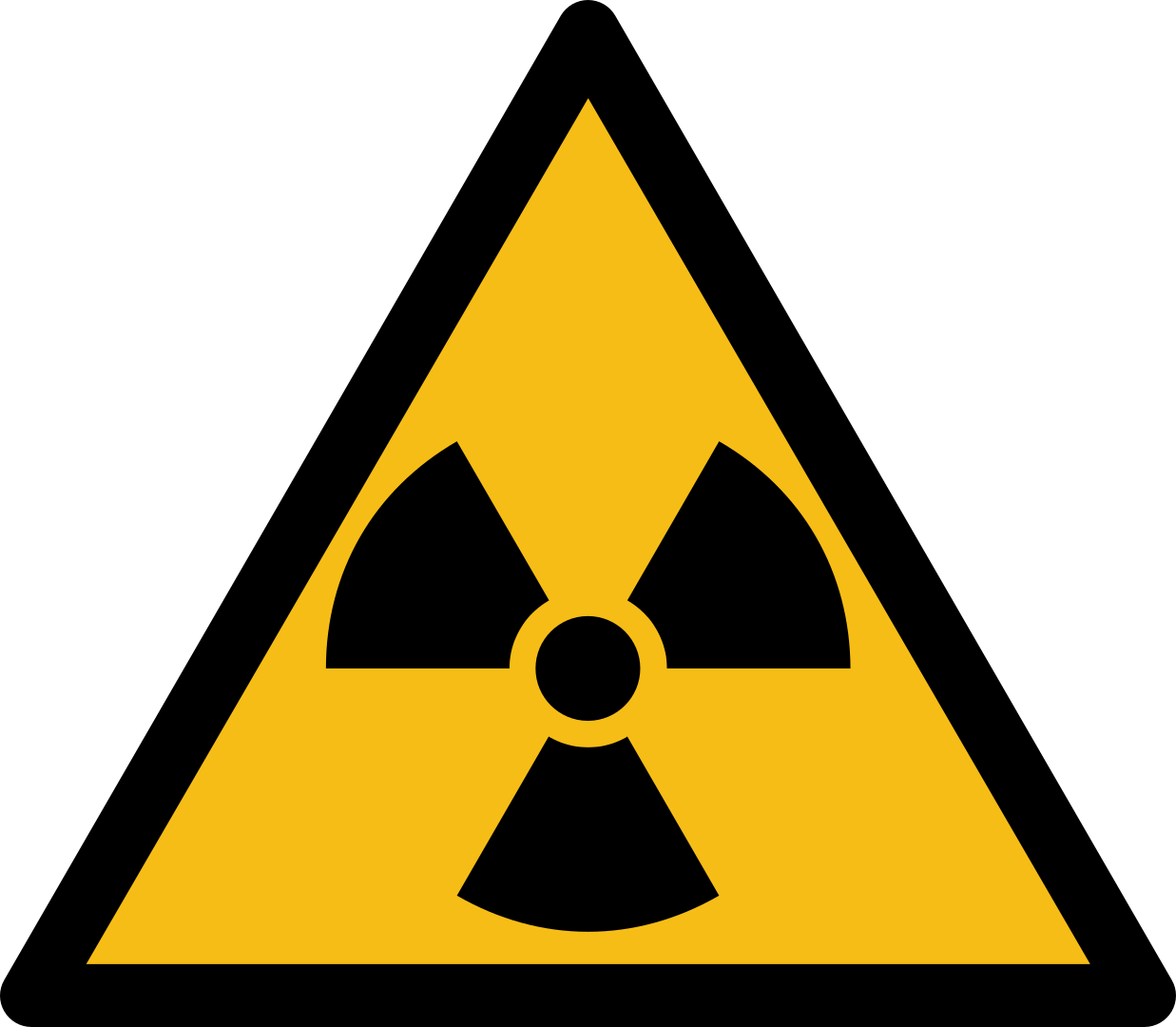

B Poorly ventilated area
C Radioactive material
D Toxic substances
Explanation: This sign is used for radioactive material.
B Only if you are wearing high visibility clothing
C Only with the permission of the lift supervisor
D You must never enter an exclusion zone
Explanation: You may only enter an exclusion zone with the permission of the lift supervisor.
B The details of the operator they will be directing
C The make and model of the vehicle they are directing
D The nearest evacuation route
Explanation: Vehicle marshallers must know the correct signals, and any additional safety procedures.