You need to answer at least 50 out of 55 questions correctly to pass the Site Transport Safety and Lifting Operations Test for Operatives and Specialists. Answers may be reviewed after each question or at the end of the test. Good luck!
List of questions in above test (quick view). Click question box to reveal correct answer.
1. Who is at risk when vehicles and mobile plants are being moved?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Accidents and injuries happen every year to operators and those in the vicinity of mobile plants and vehicles.
Explanation: Accidents and injuries happen every year to operators and those in the vicinity of mobile plants and vehicles.
2. Which ONE of the following best describes a mobile plant?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: A mobile plant is anything vehicle that can move, either by itself or through being towed.
Explanation: A mobile plant is anything vehicle that can move, either by itself or through being towed.
3. Which ONE of the following best describes an operator?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Operator in this case includes both operators and drivers.
Explanation: Operator in this case includes both operators and drivers.
4. You are not an operator, but your induction still includes information about the rules involving mobile plants. Why?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: The rules are there to avoid injury to pedestrians, too, and you must be aware of them.
Explanation: The rules are there to avoid injury to pedestrians, too, and you must be aware of them.
5. What is ONE safe way of protecting yourself from injury by a mobile plant?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Sticking to pedestrian routes is a safe way of avoiding injury.
Explanation: Sticking to pedestrian routes is a safe way of avoiding injury.
6. What is the MOST important factor to take into account when planning a vehicle route on site?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Route planning must always take into account ground conditions, as they may affect how likely a vehicle is to overturn.
Explanation: Route planning must always take into account ground conditions, as they may affect how likely a vehicle is to overturn.
7. Why are some mobile plants fitted with CCTV?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: CCTV helps expand an operator's field of vision when using large machinery. It does not guarantee they will notice pedestrians.
Explanation: CCTV helps expand an operator's field of vision when using large machinery. It does not guarantee they will notice pedestrians.
8. Who directs a crane when it is lifting a load?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Signallers directs a crane's movement. Vehicle marshallers direct moving vehicles.
Explanation: Signallers directs a crane's movement. Vehicle marshallers direct moving vehicles.
9. Why are turning areas important for safety?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Reversing creates a pedestrian hazard, and turning areas are a useful way of avoiding it.
Explanation: Reversing creates a pedestrian hazard, and turning areas are a useful way of avoiding it.
10. Which of the following will guarantee your visibility to an operator?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Nothing will guarantee that an operator will see you.
Explanation: Nothing will guarantee that an operator will see you.
11. There are usually two levels of safety zone around plant machinery. When can you enter zone 1?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Only enter zone 1 if you have received confirmation from the operator that it is safe to do so.
Explanation: Only enter zone 1 if you have received confirmation from the operator that it is safe to do so.
12. When can you enter zone 2 around plant machinery?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Zone 2 is closest to the plant. You must never enter this zone.
Explanation: Zone 2 is closest to the plant. You must never enter this zone.
13. What potentially fatal risk is created by a slewing excavator?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Plants slewing near a fixed point create a crush zone which may fatally trap people.
Explanation: Plants slewing near a fixed point create a crush zone which may fatally trap people.
14. Who can operate plant items?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: You must be authorised, trained, and competent. In some cases, you may also need to be accredited.
Explanation: You must be authorised, trained, and competent. In some cases, you may also need to be accredited.
15. When should the gap between a fixed point and a slewing plant be blocked off?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Any gap under these circumstances that is 600mm or less should be blocked off.
Explanation: Any gap under these circumstances that is 600mm or less should be blocked off.
16. Whilst operating a mobile plant, your signaller moves out of sight. What should you do?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: If you can no longer see your signaller, you must stop. Do not continue until you have located them.
Explanation: If you can no longer see your signaller, you must stop. Do not continue until you have located them.
17. How can you avoid being crushed by a slewing plant?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Do not enter the crush zone. What seems like a short exit route may in fact put you in greater danger.
Explanation: Do not enter the crush zone. What seems like a short exit route may in fact put you in greater danger.
18. A colleague offers to transport you across site on the plant they are operating. Should you accept?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: You may only ride as a passenger if the vehicle is designed to accommodate it.
Explanation: You may only ride as a passenger if the vehicle is designed to accommodate it.
19. Who is responsible for planning a lifting operation?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Your employer must designate an appointed person to plan a lifting operation.
Explanation: Your employer must designate an appointed person to plan a lifting operation.
20. What must be in place for you to supervise a crane lift?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: You must be fully trained, and have your competence verified through assessment.
Explanation: You must be fully trained, and have your competence verified through assessment.
21. How should you be informed of traffic rules on site?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Site traffic rules should be made clear during induction.
Explanation: Site traffic rules should be made clear during induction.
22. A crane signaller needs to take a bathroom break in the middle of a task. They ask you to step in, and you are not trained in the correct signals. What should you do?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: You should not act as a signaller without the correct training and competence.
Explanation: You should not act as a signaller without the correct training and competence.
23. Which THREE of the following are major risks associated with poorly planned lifting operations?
Give THREE answers
AB
C
D
E
F
Correct Answer: B, D, E
Explanation: Damage, injury, and overturning equipment are major risks run by poorly planned operations.
Explanation: Damage, injury, and overturning equipment are major risks run by poorly planned operations.
24. What should you do if you see a plant being operated over the on-site speed limit?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Report any concerns to your supervisor or employer.
Explanation: Report any concerns to your supervisor or employer.
25. What TWO things might you do if a plant is going the wrong way down a one way system?
Give TWO answers
AB
C
D
E
Correct Answer: D, E
Explanation: In an emergency, you can take action to warn the operator and others nearby. You must still inform your supervisor of the incident.
Explanation: In an emergency, you can take action to warn the operator and others nearby. You must still inform your supervisor of the incident.
26. When are you permitted to enter an exclusion zone on a site where a lift is taking place?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: You may only enter an exclusion zone with the permission of the lift supervisor.
Explanation: You may only enter an exclusion zone with the permission of the lift supervisor.
27. What are TWO important details you must know about a load before lifting it?
Give TWO answers
AB
C
D
E
Correct Answer: B, E
Explanation: Accidents can be caused by people not knowing a load's correct weight and centre of gravity.
Explanation: Accidents can be caused by people not knowing a load's correct weight and centre of gravity.
28. Which TWO of the following are important reasons to shut off the engine before exiting a vehicle?
Give TWO answers
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A, D
Explanation: Leaving the engine on wastes fuel, and could lead to accidents if you accidentally knock one of the levers whilst exiting.
Explanation: Leaving the engine on wastes fuel, and could lead to accidents if you accidentally knock one of the levers whilst exiting.
29. Which of the following is NOT an example of lifting EQUIPMENT?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Lifting equipment describes any equipment used for lifting or lowering loads or people.
Explanation: Lifting equipment describes any equipment used for lifting or lowering loads or people.
30. Which of the following is NOT an example of a lifting ACCESSORY?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Lifting accessory describes any equipment that helps attach a load to a piece of lifting equipment.
Explanation: Lifting accessory describes any equipment that helps attach a load to a piece of lifting equipment.
31. Who must be briefed about a lift plan?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: If you are involved in the operation, you must be briefed on the lift plan.
Explanation: If you are involved in the operation, you must be briefed on the lift plan.
32. Which TWO types of check must be included when inspecting lifting equipment and accessories?
Give TWO answers
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B, D
Explanation: Visual and functional checks must always form part of an inspection.
Explanation: Visual and functional checks must always form part of an inspection.
33. What else must take place in addition to regular inspections of lifting equipment and accessories?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Thorough, periodic examinations must take place as well as regular inspections.
Explanation: Thorough, periodic examinations must take place as well as regular inspections.
34. Regarding lifting equipment and accessories, what is ONE key difference between an inspection and an examination?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Examinations, unlike inspections, must produce a written report.
Explanation: Examinations, unlike inspections, must produce a written report.
35. When an examination report on lifting equipment is produced, where must it be stored?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Equipment examination reports must be stored with the equipment.
Explanation: Equipment examination reports must be stored with the equipment.
36. What is the hand signal for STOP?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Signal STOP with one open-palm hand raised directly up.
Explanation: Signal STOP with one open-palm hand raised directly up.
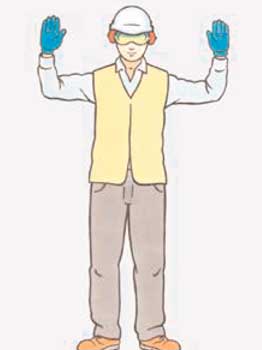
37. What is the hand signal for DANGER?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Signal DANGER with two open-palm hands raised directly up.
Explanation: Signal DANGER with two open-palm hands raised directly up.
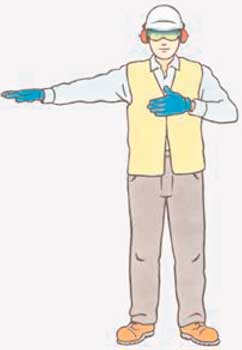
38. What is the hand signal for indicating MOVE FORWARDS
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Signal MOVE FORWARDS through a beckoning motion with an upwards-turned open palm.
Explanation: Signal MOVE FORWARDS through a beckoning motion with an upwards-turned open palm.
39. What does this signal mean?

B
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: This signal is used to show the amount of vertical distance.
Explanation: This signal is used to show the amount of vertical distance.
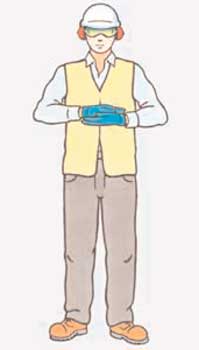
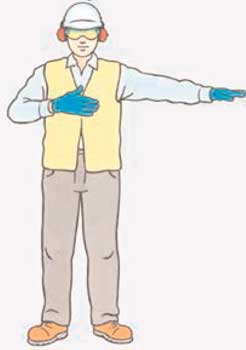
40. Which signal indicates the END of an operation?
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: This signal is used at the end of an operation.
Explanation: This signal is used at the end of an operation.
41. What does this signal mean?
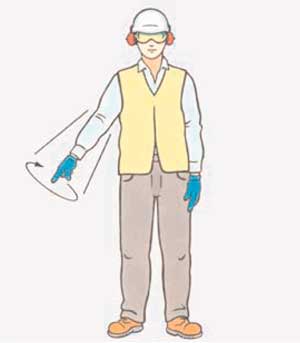
B
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: This signal indicates something must be lowered.
Explanation: This signal indicates something must be lowered.
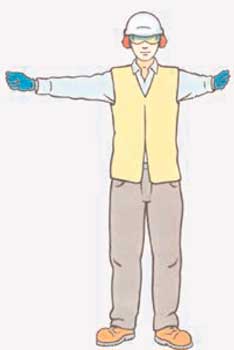
42. Which signal directs an operator LEFT?
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: This sign signals a left turn.
Explanation: This sign signals a left turn.
43. What are TWO indications that a signaller is in the CORRECT position?
Give TWO answers
AB
C
D
E
Correct Answer: D, E
Explanation: A signaller must be able to see the load, and be seen by the operator.
Explanation: A signaller must be able to see the load, and be seen by the operator.
44. When are pedestrians at MOST risk from a site vehicle?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Pedestrians are at greatest risk when a vehicle is reversing.
Explanation: Pedestrians are at greatest risk when a vehicle is reversing.
45. You are driving a vehicle around the site. What should you be looking out for?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: You should be aware of speed bumps.
Explanation: You should be aware of speed bumps.
46. You have been asked by your supervisor to use a forklift truck on shift, but you have not been trained on it. What should you do?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Always inform your supervisor if you are not trained for a task you have been assigned.
Explanation: Always inform your supervisor if you are not trained for a task you have been assigned.
47. What must a vehicle marshaller know before they can safely begin work?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Vehicle marshallers must know the correct signals, and any additional safety procedures.
Explanation: Vehicle marshallers must know the correct signals, and any additional safety procedures.
48. How should the risk of a vehicle overturning be mitigated when that risk is high?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Roll-over protective structures (ROPS) should be fitted if the risk of overturning is high.
Explanation: Roll-over protective structures (ROPS) should be fitted if the risk of overturning is high.
49. Which type of accident is common when using dumpers?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: C
Explanation: Overturning is a common accident when using dumpers.
Explanation: Overturning is a common accident when using dumpers.
50. Your colleague informs you that your vehicle has a flat tyre. What does this mean?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Flat tires can render a vehicle unsafe to drive.
Explanation: Flat tires can render a vehicle unsafe to drive.
51. What one factor may increase the risk of a telehandler overturning?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: Telehandlers are more likely to overturn if driven too fast.
Explanation: Telehandlers are more likely to overturn if driven too fast.
52. What are TWO conditions which must be met for you to operate plant?
Give TWO answers
AB
C
D
E
Correct Answer: A, D
Explanation: Plant operators must be trained, competent, and authorised.
Explanation: Plant operators must be trained, competent, and authorised.
53. How should you load a vehicle to reduce the risk of it overturning?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: A
Explanation: To reduce the risk of overturning, you should distribute a vehicle's load evenly.
Explanation: To reduce the risk of overturning, you should distribute a vehicle's load evenly.
54. How often should equipment used for lifting people be THOROUGHLY examined?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: B
Explanation: Equipment used for lifting people must be thoroughly examined every 6 months.
Explanation: Equipment used for lifting people must be thoroughly examined every 6 months.
55. Vehicle movement on site is best controlled by who?
Give ONE answer
AB
C
D
Correct Answer: D
Explanation: Vehicle marshallers should be directing vehicles on site.
Explanation: Vehicle marshallers should be directing vehicles on site.